Studien- / Diplom- /Masterarbeit, ET / MT / IST / NES / BMT / CS / POL
Motivation
Physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) such as MaxwellNet provide an efficient forward model for electromagnetic wave propagation and have been demonstrated for optical diffraction tomography. By incorporating physical laws directly into the learning process, PINNs enable forward modeling without relying on labeled training datasets. A reliable forward model is a fundamental prerequisite for accurate three-dimensional reconstruction. Existing MaxwellNet-based models enable fast prediction of scattered fields from refractive-index distributions. However, their applicability under different geometric transformations and experimental conditions has not been systematically investigated. In this topic, a MaxwellNet model will be reproduced and extended, and its prediction accuracy will be quantitatively evaluated using numerical phantoms and reference solvers. The influence of geometric transformations, numerical interpolation, and model assumptions on the predicted fields will be systematically analyzed.
(a) Forward process
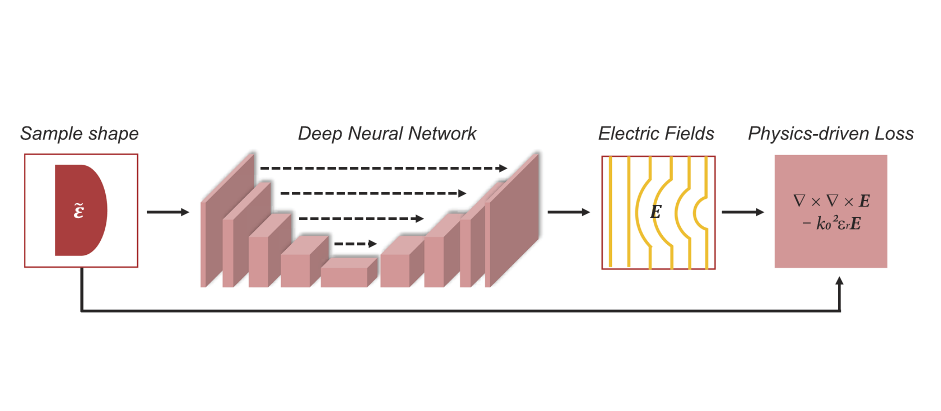
(b) Reconstruction process
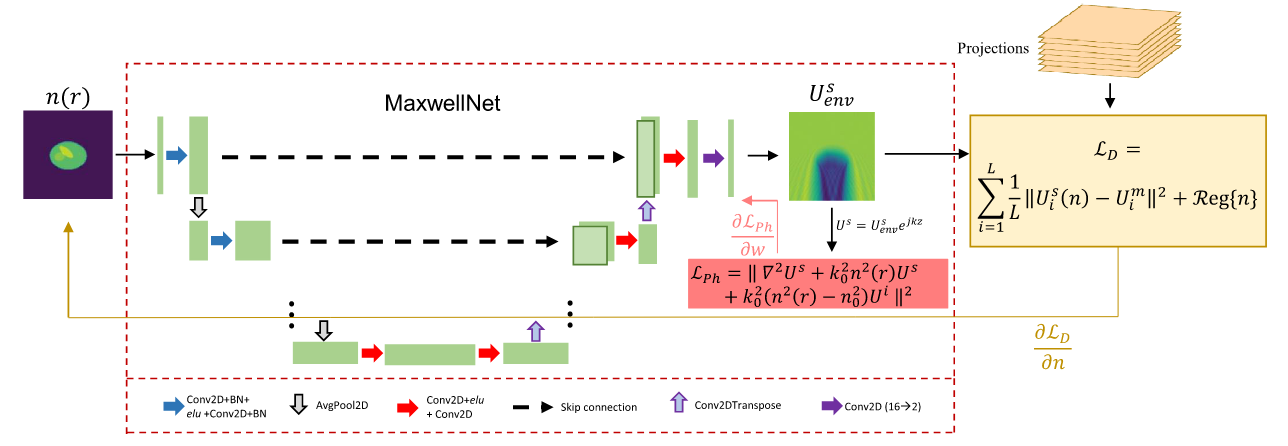
Task
- Reproduction of a MaxwellNet-based forward modeling framework
- Extension of the forward model to different geometric transformations and configurations
- Evaluation of forward-model performance using numerical phantoms and reference solvers
Keywords
Physics-informed neural networks, MaxwellNet, forward modeling, optical tomography, Python, PyTorch
Contact
Dipl.-Ing. Bin Yang, BAR 116
