ET | INF | MT | PHY | POL | RES
Motivation
Diffuser based imaging is a recent topic in computational optics. The diffuser generates a unique pseudorandom speckle pattern for every point within a volumetric field-of-view on an image plane. By solving the inverse problem, the 3D scene can be reconstructed fast computationally by using neural networks. In conjunction with imaging waveguides, this enables the realization of single shot 3D microendoscopes.
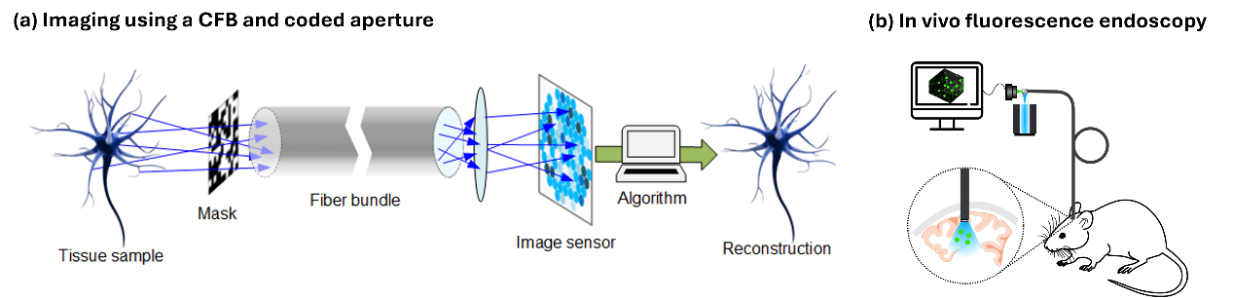
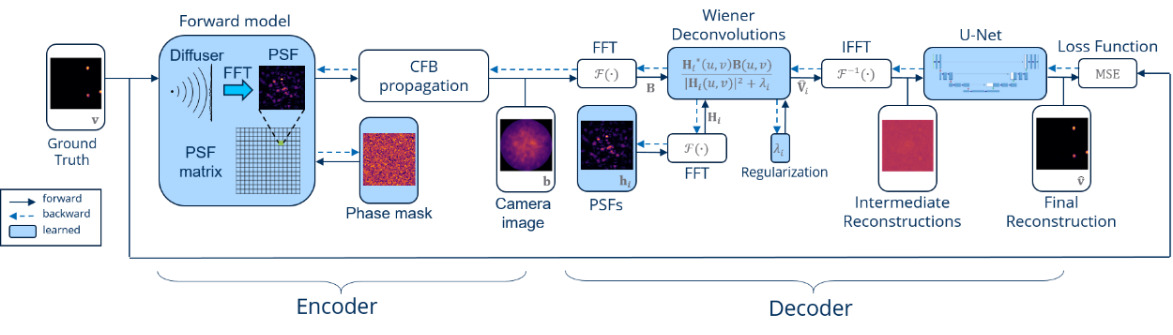
Furthermore, the optical system can be optimized in conjunction with a decoding physics-informed neural network in an end-to-end training approach. After finishing the training process, optimized phase masks can be adapted by a spatial light modulator to validate it and characterize the imaging system. Moreover, recent neural network architectures based on attention are implemented for image reconstruction tasks and can be combined with spatially-varying deconvolution by Wiener filters.
Tasks
- End-to-End training of a coded aperture and a physics-informed neural network decoder
- Experimental validation of optimized phase masks with a spatial light modulator
- Implementation of current attention-based network architecture for physics-informed neural network image reconstruction
- Characterization of the optimized optical system
Contact
Tom Glosemeyer tom.glosemeyer@tu-dresden.de